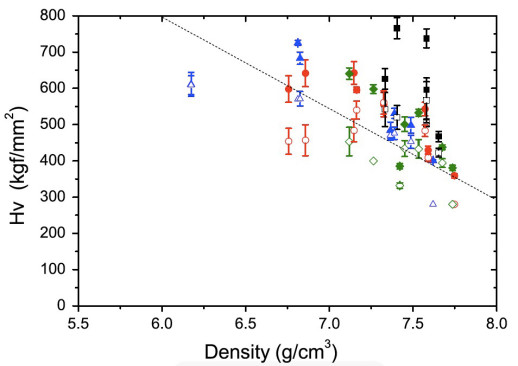
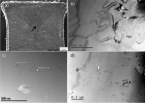
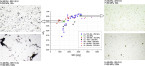
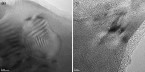
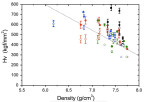
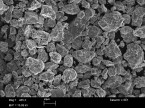
Net-shape compaction of a nanocrystalline ball-milled commercial Fe-1.5 wt pct Mo powder was done via spark plasma sintering (SPS) and capacitor discharge sintering (CDS). A detailed microstructure analysis, performed by X-ray diffraction–whole powder pattern modeling (XRD-WPPM), shows that CDS, owing to the faster sintering conditions, retains a much finer and more uniform microstructure with dislocations uniformly distributed inside the nanocrystalline grains. Conversely, SPS causes dislocations to pile up and extensive grain growth to occur, especially when high sintering temperatures are employed.
© The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society and ASM International 2009